Thermo Fisher Scientific › Electron Microscopy › Electron Microscopes › 3D Visualization, Analysis and EM Software › Use Case Gallery
High-resolution 3D images of organelles are of paramount importance in cellular biology. Although light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) have provided the standard for imaging cellular structures, they cannot provide 3D images.
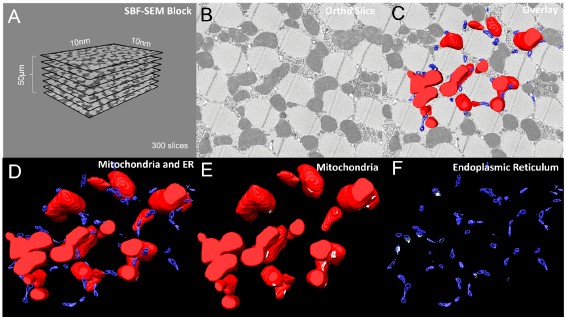
However, recent technological advances such as serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) provide the tools to create 3D images for the ultrastructural analysis of organelles. Here, we describe a standardized protocol using the visualization software, Amira, to quantify organelle morphologies in 3D, thereby providing accurate and reproducible measurements of these cellular substructures. We demonstrate applications of SBF-SEM and Amira to quantify mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) structures.
High-quality images obtained by SBF-SEM or other data acquisition methods can be reconstructed in 3D using Amira. Amira is a user-friendly application that allows 2D-image slices, known as orthos, to be digitally analyzed, segmented, color-coded, and rendered for 3D reconstruction.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.